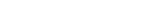digital fake id
Introduction: The Rise of Digital Fake IDs in a Hyperconnected World
As digital transformation accelerates in every sector of life, traditional forms of identification—physical IDs such as driver’s licenses, passports, and student IDs—are being replaced or complemented by their digital counterparts. One of the most intriguing (and controversial) manifestations of this shift is the emergence of digital fake IDs. In a world where anonymity is highly valued, digital fake IDs provide users with new ways to access services, safeguard their privacy, or, unfortunately, to bypass legal boundaries.
But what exactly is a digital fake ID? How does it work, and who uses it? This article will explore these questions by examining the key features of digital fake IDs, analyzing the market for such services, and discussing their appeal to various audiences. We'll also delve into the ethical, legal, and societal implications surrounding their use.
What Is a Digital Fake ID?
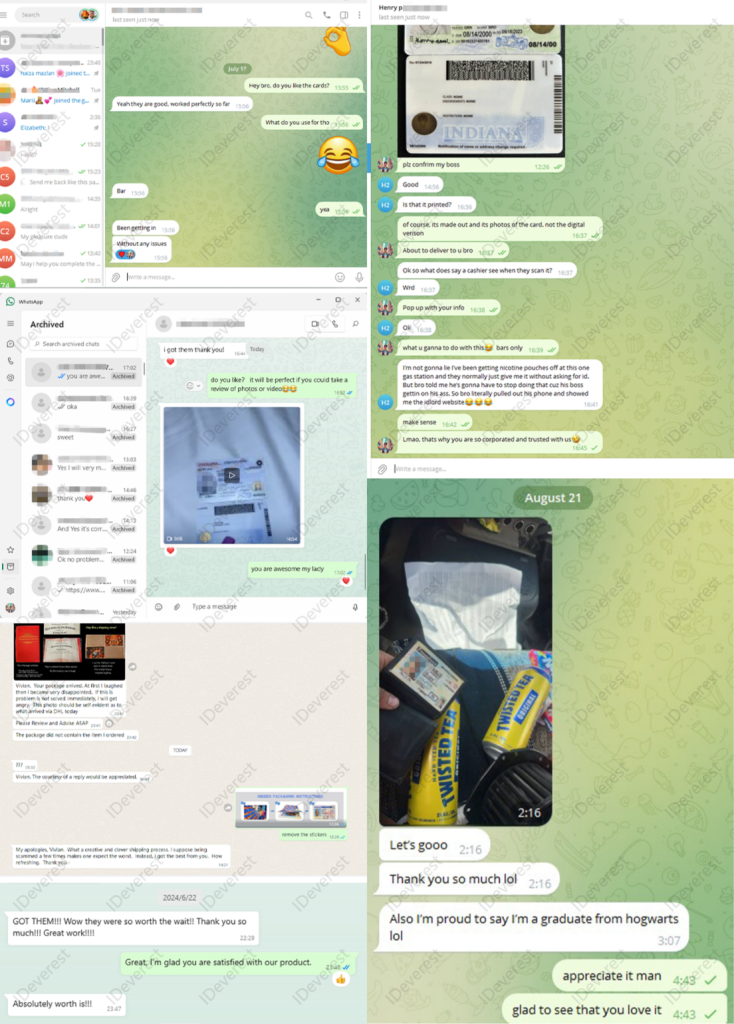
A digital fake ID is an electronically created identification that mimics a real document, such as a driver's license or student ID, to be used primarily online. These IDs are typically created through sophisticated graphic design and data manipulation techniques to resemble legitimate government or institution-issued documents. The purposes for which they are used vary widely, from accessing restricted content or websites, to participating in online forums or activities anonymously, to circumventing restrictions on age or location.
How Are Digital Fake IDs Made?
The process of creating digital fake IDs often involves using specialized software like Adobe Photoshop or more dedicated ID-generating applications that come pre-loaded with templates. These applications allow users to easily manipulate photos, change text, add barcodes, and even include holographic seals to mimic the appearance of legitimate identification.
Key Features of Digital Fake IDs:
- Customizable Templates: High-quality templates that match various types of government-issued IDs, with features like holograms, barcodes, and watermarks.
- Realistic Design Elements: Use of advanced design tools to replicate official fonts, layouts, and security features.
- Barcode and Magnetic Strip Encoding: For the most realistic experience, digital fake IDs may include scannable barcodes or encoded magnetic strips.
- Personalization Options: The ability to input customized personal data, such as a user's name, date of birth, and address.
- Digital Delivery: Fake IDs are primarily delivered via email or download links as digital files that can be used online or printed out.
While physical fake IDs have existed for decades, the digital versions have the unique advantage of existing entirely in the digital realm, where their creation and distribution are quicker, easier, and less risky than their physical counterparts.
Market Analysis: The Rise of the Digital Fake ID Industry
A Lucrative and Growing Market
The digital fake ID industry is booming, driven by increasing demand across a variety of sectors. Market research shows that there is a steady rise in the use of digital fake IDs, particularly among tech-savvy youth, privacy advocates, and individuals from restricted or oppressive environments. Several factors contribute to the rising demand:
- Digitalization of Services: As more services go online, there is an increased need for identification verification, opening the door for those looking to use digital fake IDs to access restricted services or protect their privacy.
- Increased Online Restrictions: Many countries have started implementing stringent regulations around online activities such as gaming, streaming, and accessing adult content. Digital fake IDs offer a workaround for these restrictions.
- E-commerce and Online Shopping: Many online stores have age restrictions for purchasing certain products (e.g., alcohol, tobacco, or restricted-access pharmaceuticals). Digital fake IDs can be used to bypass such limitations.
Geographic Distribution of the Market
The market for digital fake IDs is concentrated in regions with high internet penetration rates and where digital services are heavily regulated. North America, Europe, and parts of Asia (particularly China and South Korea) are hotspots for digital fake ID usage due to government-imposed restrictions on various digital activities.
- North America: The United States and Canada have strict age verification laws for alcohol, tobacco, and certain online services (such as gambling and adult websites). Digital fake IDs are often used by underage consumers to access these services.
- Europe: Countries like the UK and Germany have strong digital privacy regulations. In some cases, digital fake IDs are used to anonymize personal information in contexts like social media or online dating.
- Asia: In regions with restrictive internet policies, such as China, digital fake IDs are used to bypass government-imposed firewalls and access restricted content.
Target Audience for Digital Fake IDs
The target demographic for digital fake IDs is broad, encompassing a range of users who each have their unique motivations. Below is a detailed breakdown of the key audience segments:
1. Tech-Savvy Youth
Perhaps the largest demographic, tech-savvy youth (ages 16-25) are frequent users of digital fake IDs. These users primarily seek access to age-restricted services such as streaming platforms, online gaming communities, and even online casinos. For many, it’s about pushing the boundaries of online access, often without fully understanding the legal ramifications.
Motivations:
- Access to online entertainment platforms (movies, music, games).
- Circumventing age restrictions for buying alcohol, tobacco, and other regulated items.
- Privacy protection and anonymity in forums, social media, and online chatrooms.
2. Privacy Advocates and Cybersecurity Enthusiasts
A growing number of people are using digital fake IDs to protect their online identity in an era of rampant data collection and privacy breaches. Privacy advocates seek to use fake identities to avoid having their personal data tracked by advertisers, tech companies, and even governments.
Motivations:
- Avoidance of online tracking and data harvesting.
- Safeguarding personal information from hackers, scammers, and identity thieves.
- Anonymity in online discussions, especially in politically sensitive environments.
3. Online Freelancers and Gig Economy Workers
For some freelance workers, particularly in countries with stringent regulations, having a digital fake ID can be a way to gain access to international platforms where registration requires a verified ID from another country. This is especially common in regions where freelancers or gig workers are limited by local regulations or licensing requirements.
Motivations:
- Bypassing geographic restrictions to access platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, or Amazon Mechanical Turk.
- Avoiding high tax rates or stringent regulatory compliance in their home country.
- Using alternate identities for multi-accounting or platform evasion.
4. Citizens of Restricted or Authoritarian Regimes
In many authoritarian regimes, citizens face censorship and limitations on what they can access online. Digital fake IDs allow individuals in such countries to break through firewalls and access blocked websites, communicate freely, and participate in political activism without fear of repercussion.
Motivations:
- Access to uncensored information.
- Engaging in online activism and organizing protests.
- Anonymous communication on social media platforms.
Ethical and Legal Concerns Surrounding Digital Fake IDs
While digital fake IDs provide solutions to certain problems related to privacy, access, and freedom of information, they also raise several ethical and legal issues. Understanding these implications is critical for both users and service providers.
1. Legal Risks for Users
In most countries, using a fake ID, whether physical or digital, is illegal. Users can face heavy fines, criminal charges, and even jail time if caught using a fake ID for fraudulent purposes. Online platforms and governments are ramping up security measures to detect and punish fake ID use, especially in sectors where age verification is legally mandated (e.g., online gambling and adult content).
2. Impact on Online Fraud and Identity Theft
Digital fake IDs can also exacerbate problems related to online fraud and identity theft. Criminals can use fake IDs to create fraudulent accounts, which are then used for illegal activities such as scamming, phishing, and even money laundering. Additionally, fake ID use undermines the integrity of digital systems and online services, potentially harming legitimate users and organizations.
3. Ethical Dilemmas for Service Providers
For companies offering digital fake ID services, ethical dilemmas are ever-present. On the one hand, providing fake IDs may give users tools to protect their privacy and bypass unjust censorship; on the other hand, these services can facilitate illegal activities and be misused by bad actors.
How Digital Fake IDs Are Used: Common Applications
Digital fake IDs are utilized across a variety of online platforms, often in ways that are not immediately obvious. Below are some common areas where digital fake IDs find application:
1. Accessing Age-Restricted Content
Websites that sell products or services that require age verification (e.g., online casinos, alcohol vendors, or adult content providers) are prime targets for digital fake ID use. Users who are underage often use these IDs to bypass the verification process.
2. E-commerce Fraud
Another common use is within the e-commerce industry, where digital fake IDs can be employed to carry out fraudulent purchases or to access restricted goods. Some users also create fake IDs to open multiple accounts on certain platforms, benefitting from first-time user promotions or offers.
3. Social Media and Online Communities
Certain social media platforms require verification of identity to access specific features or join exclusive groups. Users may employ digital fake IDs to maintain anonymity or to participate in activities without revealing their real identity.
The Future of Digital Fake IDs: Trends and Predictions
As technology advances, so too will the methods for creating and detecting digital fake IDs. Several trends suggest that this market will continue to grow, but also that new security measures will emerge to counteract their use.
- Increased Use of Biometric Verification: As more platforms adopt biometric verification (e.g., facial recognition, fingerprint scanning), digital fake IDs will need to evolve to include more sophisticated features that mimic or bypass biometric systems.
- Blockchain-Based Digital ID Systems: Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way identities are verified online. With decentralized and immutable ledgers, blockchain could help eliminate fake IDs by creating tamper-proof digital identities.
- Artificial Intelligence in ID Verification: AI-based systems are already being deployed to detect fake IDs. As these systems become more advanced, they will be able to more easily identify inconsistencies in digital fake IDs, reducing their effectiveness over time.
Conclusion: The Double-Edged Sword of Digital Fake IDs
Digital fake IDs represent a complex intersection of privacy, access, legality, and ethics. While they offer users a way to maintain anonymity, access restricted services, and safeguard personal data, they also open the door to a host of legal and ethical issues. As the digital fake ID market grows, both users and regulators will need to adapt to the evolving landscape, ensuring that privacy and freedom are balanced with security and legality.
Understanding the intricacies of digital fake IDs allows us to better navigate this controversial space and anticipate future developments in online identity verification. While their use may continue to rise, advancements in AI, biometrics, and blockchain will play a critical role in shaping the future of digital identification and privacy.
 Fake ID buyers
Fake ID buyers
 Scannable Fake ID
Scannable Fake ID
 Custom Fake Texas ID
Custom Fake Texas ID
 Georgia ID Card
Georgia ID Card
 perfect fake id
perfect fake id
 digital fake id
digital fake id